Spiral Guide Algorithm [V2]
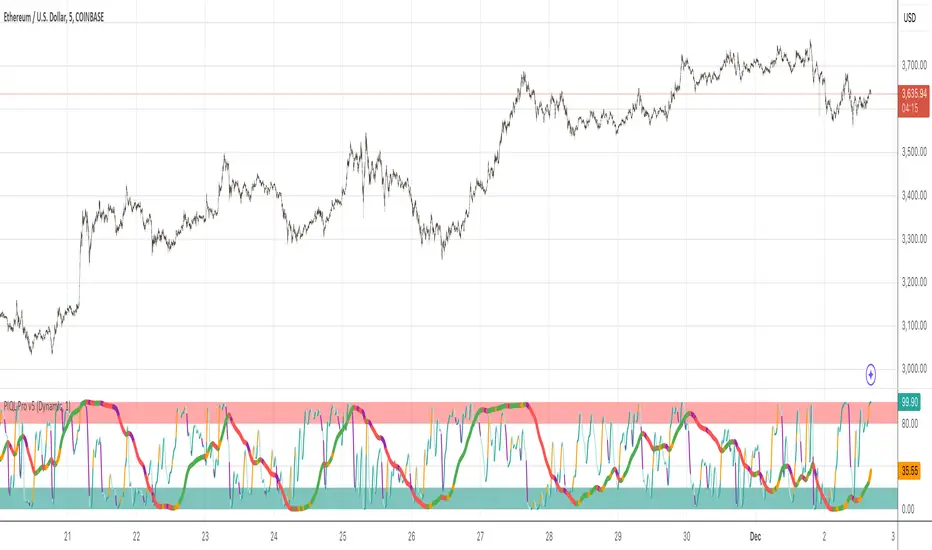
At its core, the Spiral Guide Algorithm is a low noise, un-bounded, oscillating cycle indicator designed to capture state change within a non-Gaussian distribution.
The idea, design, and application of the Spiral Guide Algorithm is rooted in first principles from four core areas of study, and in application proves to be an excellent trend following tool.
The Spiral Guide Algorithm produces and visualizes three principal components. Below we will cover each of those areas, as well as, how to apply this algorithm in trade analysis.
Principal Components
1. SGA Signal = waveform fundamental signal line
2. SGA Filtered Signal= finite impulse response filter of the SGA signal
3. SGA Histogram= delta between SGA signal and SGA filtered signal
Theory of Operation
1. Digital Signal Processing (DSP)
a. The SGA applies a DSP technique used in wireless transmission that decomposes a waveform into discrete components and then quantifies the interaction between each of those components.
2. Complex Systems Theory
a. In complex systems the tail often wags the dog and so SGA focuses not on the average of the distribution, but on the edges.
3. Game Theory
a. Positive feedback drives large changes from historical extremes, so targeting points of extreme oscillation offers the best chance of capturing large changes in the distribution.
4. Auction Theory
a. We know the auction process cycles between two phases:
i. At value
ii. Discovering value
b. SGA is designed to capture much of the “value discovery” phase between two “at value” areas.
Derivatives
1. When the SGA signal line is above 0 the time frame is up-trending
2. When the SGA signal line is below 0 the time frame is down-trending
3. A fundamental time frame shift is occurring when SGA signal line crosses 0
4. The ratio of SGA signal line time above 0 vs time below 0 will expose the current time frame bias (long, short, flat)
Application
1. Trades are signaled when the SGA signal line crosses the SGA filtered signal, and the trade is confirmed when the SGA filtered signal changes state.
2. Trades can be entered when the SGA signal line crosses 0.
3. SGA should align with the following before entering a trade: Structure, Cycles, Fractals.
4. The histogram is used for detecting divergence.
When and Where
1. Due to the large number of sample sets needed to calculate the SGA signal line, the SGA is designed for intraday charting.
2. Monitor multiple time frames around entry and exit time frame to satisfy the fractal requirements. As a rule, a 3-5x fractal above and below the entry and exit time frame is needed to align cycles.
3. For example:
a. Tick data or 1 second
b. 1 min
c. 5 min (entry/exit)
d. 15 min
4. This algorithm sees success in markets that are not mean reversion biased.
a. Trending markets with high volatility provide the best results.
#Added more functionality to adjust SGA indicator:
- Enable/disable SGA signal lines
- Enable/disable SGA histogram
- Divergence detection both positive and negative
- Redesigned histogram calculation to reduce false signals and increase tradeability
- SGA/Hist Max/Min enable/disable
- Long/Short Coloring
- SGA Fast
- SGA Very Fast
Corrected alert print output
- Improved Settings MenuAdded OTF Heat MapAdded New Alert FunctionsRe-factored Core RoutinesAdded Signal Stat BoxAdded Histogram Stat Box
- Corrected Alert Logic
- Updated Alert Menu
- updated script to include only user requested features
- improved loading times
- LTS SGA Version
- Refactored most of of the code base
- Updated to Pinescript V5
- Updated Menu Section
- Added Liner Regression Channels
- Added SGA Prime Indicator
- Updated Alert Functionality
- Fixed SGA Prime issue caused by TV backend
- Added Strategy Visualizations
- Added SGA Trend Confirm Tool
- Removed Stat Boxes
- Updated SGA Trend Confirm
- Added SGA Prime plot label
- Added SGA Prime Strategy Settings & Alerts
- Added Trend Confirm Plots
[*} Updated Trend Confirm Function
- Corrected Data Input Formula
- Corrected bug in TC
- Added SGA TC Color Change Plots
- Corrected Trend Confirm Plots
- Added Rev Control
- Added Trend Confirm Alerts
- Removed SGA Crossing Zero Exit Filter
- Added Bot ID Selection In Settings
- Corrected Alerts "side":"exit" problem
- Updated TC Plot to Show When No Bias Present
- Re-organized menu structure
- Added SGA Prime forced alert
- Unknown TV bug; reverting to build 1.2
- Removed unused plots due to hitting limit
- Re-organized menu structure
- Added SGA Prime forced alert
- Updated SGA Color Alerts
- removed extra code
نص برمجي للمستخدمين المدعوين فقط
يمكن فقط للمستخدمين الذين تمت الموافقة عليهم من قبل المؤلف الوصول إلى هذا البرنامج النصي. ستحتاج إلى طلب الإذن والحصول عليه لاستخدامه. يتم منح هذا عادةً بعد الدفع. لمزيد من التفاصيل، اتبع تعليمات المؤلف أدناه أو اتصل ب leerider مباشرة.
لا توصي TradingView بالدفع مقابل برنامج نصي أو استخدامه إلا إذا كنت تثق تمامًا في مؤلفه وتفهم كيفية عمله. يمكنك أيضًا العثور على بدائل مجانية ومفتوحة المصدر في نصوص مجتمعنا.
تعليمات المؤلف
Get a FREE Spiral Guide Algorithm (PIQL Pro v5) trial:
primeiqlabs.com/step/piql-pro-free-trial/
Join our free Discord server:
discord.gg/invite/primeiqlabs
إخلاء المسؤولية
نص برمجي للمستخدمين المدعوين فقط
يمكن فقط للمستخدمين الذين تمت الموافقة عليهم من قبل المؤلف الوصول إلى هذا البرنامج النصي. ستحتاج إلى طلب الإذن والحصول عليه لاستخدامه. يتم منح هذا عادةً بعد الدفع. لمزيد من التفاصيل، اتبع تعليمات المؤلف أدناه أو اتصل ب leerider مباشرة.
لا توصي TradingView بالدفع مقابل برنامج نصي أو استخدامه إلا إذا كنت تثق تمامًا في مؤلفه وتفهم كيفية عمله. يمكنك أيضًا العثور على بدائل مجانية ومفتوحة المصدر في نصوص مجتمعنا.
تعليمات المؤلف
Get a FREE Spiral Guide Algorithm (PIQL Pro v5) trial:
primeiqlabs.com/step/piql-pro-free-trial/
Join our free Discord server:
discord.gg/invite/primeiqlabs