OPEN-SOURCE SCRIPT
TASC 2023.05 Cong Adaptive Moving Average
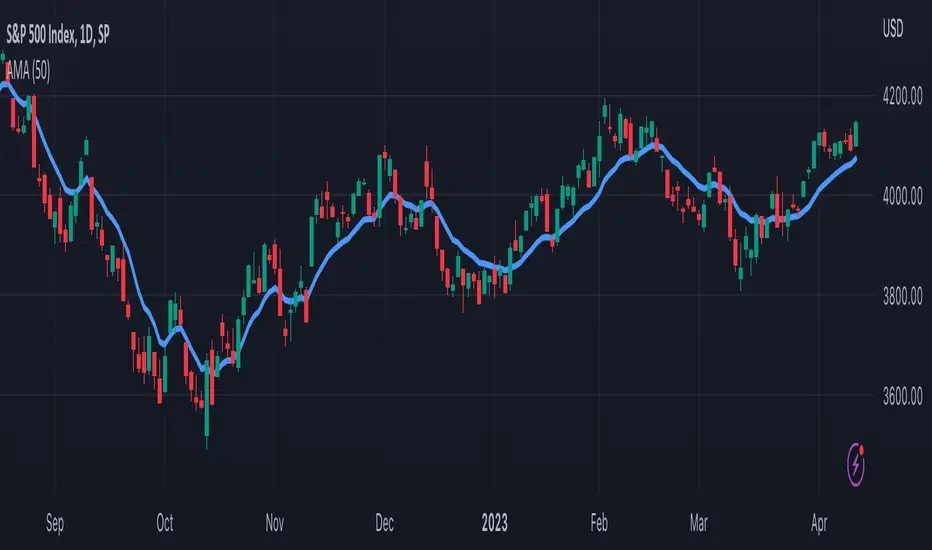
█ OVERVIEW
TASC's May 2023 edition of Traders' Tips features an article titled "An Adaptive Moving Average For Swing Trading" by Scott Cong. The article presents a new adaptive moving average (AMA) that adjusts its parameters automatically based on market volatility. The AMA tracks price closely during trending movements and remains flat during congestion areas.
█ CONCEPTS
Conventional moving averages (MAs) use a fixed lookback period, which may lead to limited performance in constantly changing market conditions. Perry Kaufman's adaptive moving average, first described in his 1995 book Smarter Trading, is a great example of how an AMA can self-adjust to adapt to changing environments. Scott Cong draws inspiration from Kaufman's approach and proposes a new way to calculate the AMA smoothing factor.
█ CALCULATIONS
Following Perry Kaufman's approach, Scott Cong's AMA is calculated progressively as:
AMA = α * Close + (1 − α) * AMA(1),
where:
The smoothing factor determines the performance of AMA. In Cong's approach, it is calculated as:
α = Result / Effort,
where:
As the price range is always no greater than the total journey, α is ensured to be between 0 and 1.
TASC's May 2023 edition of Traders' Tips features an article titled "An Adaptive Moving Average For Swing Trading" by Scott Cong. The article presents a new adaptive moving average (AMA) that adjusts its parameters automatically based on market volatility. The AMA tracks price closely during trending movements and remains flat during congestion areas.
█ CONCEPTS
Conventional moving averages (MAs) use a fixed lookback period, which may lead to limited performance in constantly changing market conditions. Perry Kaufman's adaptive moving average, first described in his 1995 book Smarter Trading, is a great example of how an AMA can self-adjust to adapt to changing environments. Scott Cong draws inspiration from Kaufman's approach and proposes a new way to calculate the AMA smoothing factor.
█ CALCULATIONS
Following Perry Kaufman's approach, Scott Cong's AMA is calculated progressively as:
AMA = α * Close + (1 − α) * AMA(1),
where:
- Close = Close of the current bar
- AMA(1) = AMA value of the previous bar
- α = Smoothing factor between 0 and 1, defined by the lookback period
The smoothing factor determines the performance of AMA. In Cong's approach, it is calculated as:
α = Result / Effort,
where:
- Result = Highest price of the n period − Lowest price of the n period
- Effort = Sum(TR, n), where TR stands for Wilder’s true range values of individual bars of the n period
- n = Lookback period
As the price range is always no greater than the total journey, α is ensured to be between 0 and 1.
نص برمجي مفتوح المصدر
بروح TradingView الحقيقية، قام مبتكر هذا النص البرمجي بجعله مفتوح المصدر، بحيث يمكن للمتداولين مراجعة وظائفه والتحقق منها. شكرا للمؤلف! بينما يمكنك استخدامه مجانًا، تذكر أن إعادة نشر الكود يخضع لقواعد الموقع الخاصة بنا.
Tools and ideas for all Pine coders: tradingview.com/u/PineCoders/
TASC: traders.com/
TASC: traders.com/
إخلاء المسؤولية
لا يُقصد بالمعلومات والمنشورات أن تكون، أو تشكل، أي نصيحة مالية أو استثمارية أو تجارية أو أنواع أخرى من النصائح أو التوصيات المقدمة أو المعتمدة من TradingView. اقرأ المزيد في شروط الاستخدام.
نص برمجي مفتوح المصدر
بروح TradingView الحقيقية، قام مبتكر هذا النص البرمجي بجعله مفتوح المصدر، بحيث يمكن للمتداولين مراجعة وظائفه والتحقق منها. شكرا للمؤلف! بينما يمكنك استخدامه مجانًا، تذكر أن إعادة نشر الكود يخضع لقواعد الموقع الخاصة بنا.
Tools and ideas for all Pine coders: tradingview.com/u/PineCoders/
TASC: traders.com/
TASC: traders.com/
إخلاء المسؤولية
لا يُقصد بالمعلومات والمنشورات أن تكون، أو تشكل، أي نصيحة مالية أو استثمارية أو تجارية أو أنواع أخرى من النصائح أو التوصيات المقدمة أو المعتمدة من TradingView. اقرأ المزيد في شروط الاستخدام.